PRP vs. Stem Cell Therapy: Choosing the Right Regenerative Treatment for You

Reed Berglund is a passionate advocate for wellness and an…
Regenerative medicine, like PRP vs Stem Cell therapy, is transforming the way we approach injuries and degenerative conditions, shifting the focus from managing symptoms to potentially healing the underlying damage. As a lifelong athlete and someone deeply embedded in the sports community, I’ve always been on the lookout for treatments that can prevent injuries and the dreaded “knife.” Recently, more and more people in our community—whether they’re soccer enthusiasts, tennis or padel aficionados, or dedicated to the grueling demands of CrossFit and Hyrox—have been exploring innovative therapies to help manage their injuries. The spotlight has increasingly turned to Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) and Stem Cell Therapy, two promising regenerative therapies that offer hope beyond traditional surgical interventions.
As interest grows, so does the curiosity about how these treatments work and which might be more suitable depending on the type of injury. In this article, we’re diving deep into the world of PRP and Stem Cell Therapy. With insights from local experts and stories from fellow athletes within our community, we’ll explore the distinct capabilities and applications of each therapy. This guide is crafted to help you understand the nuances between PRP and stem cells, empowering you with knowledge to make informed decisions about your health and recovery options. Join us as we navigate through the intricacies of these groundbreaking treatments, illuminated by professional insights and real-life experiences from those who live and breathe sports.
Understanding PRP Therapy
Definition of PRP Therapy and Its Role in Regenerative Medicine
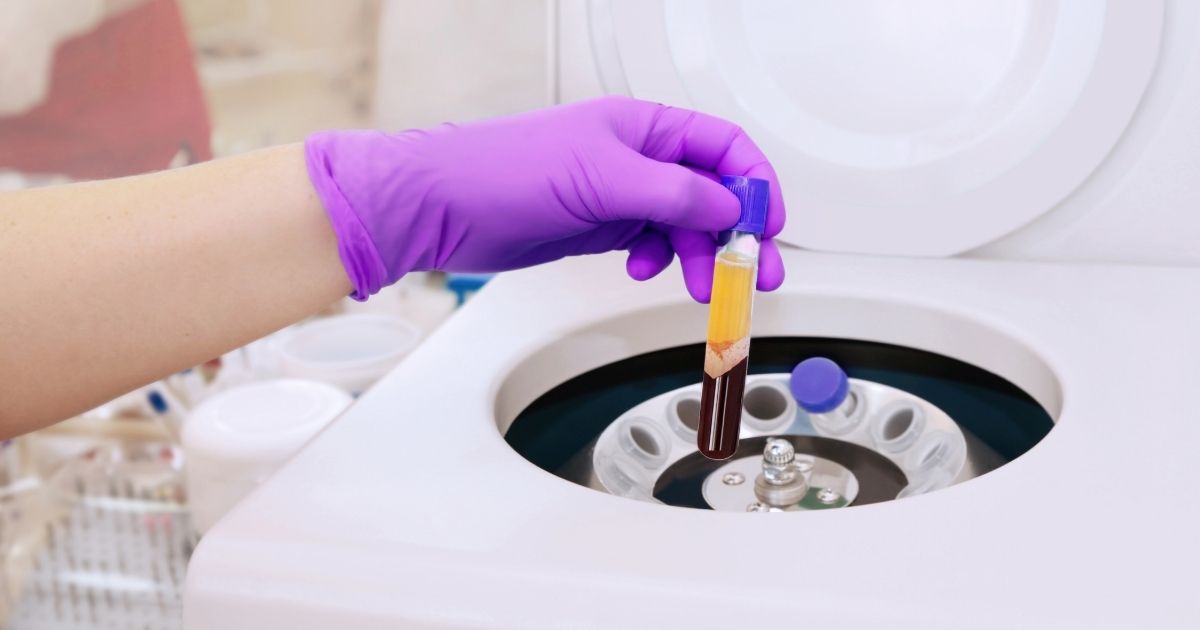
Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy is a form of regenerative medicine that utilizes the body’s own healing mechanisms to accelerate the repair of injured tissues. PRP is derived from the patient’s own blood and is especially rich in growth factors that play a crucial role in healing and tissue regeneration. This therapy capitalizes on the natural biological components of blood to enhance recovery, making it a popular choice in the sports community and beyond for its minimally invasive nature and effectiveness.
How PRP vs Stem Cell Works: Process from Blood Collection to Re-injection
The procedure for PRP therapy begins with the collection of a small amount of the patient’s blood, similar to a routine blood test. This blood is then placed in a centrifuge, where it is spun at high speeds. This process separates the blood components and concentrates the platelets in the plasma, creating the platelet-rich plasma. This concentrated PRP contains up to 5 times the number of growth factors found in normal blood.
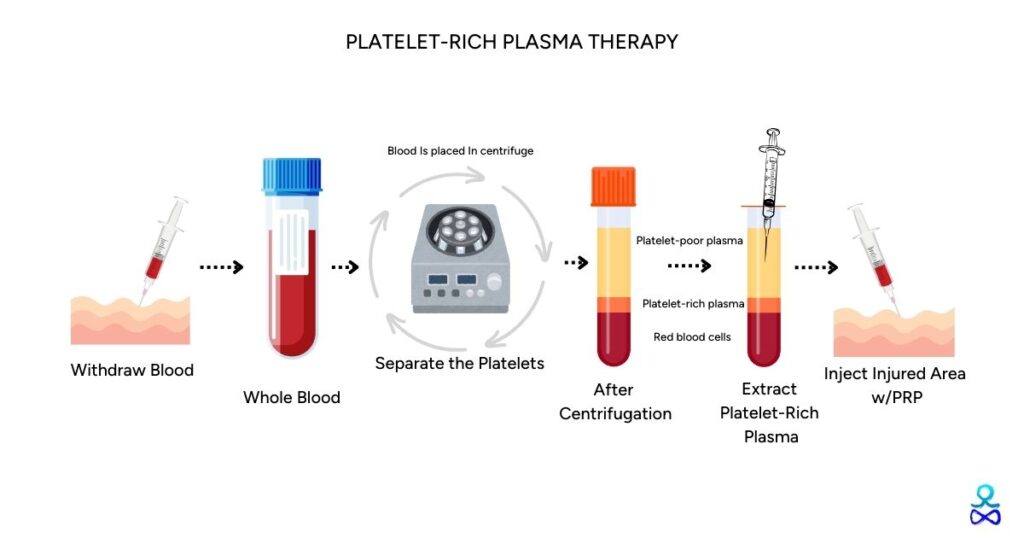
Once the PRP is prepared, it is re-injected directly into the injured area. This direct injection increases the concentration of growth factors precisely where they are needed, kickstarting and significantly enhancing the body’s natural healing processes.
Common Applications of PRP Therapy and Its Effectiveness
PRP therapy is commonly used to treat a variety of sports injuries, orthopedic conditions, and musculoskeletal problems. It is particularly effective in treating conditions such as:
- Tendon injuries, including tennis elbow and Achilles tendonitis.
- Ligament sprains and muscle injuries that are common in athletes.
- Joint pain and instability, including knee osteoarthritis and other degenerative joint diseases.
The effectiveness of PRP therapy lies in its ability to reduce inflammation, improve joint function, and promote the growth of new cartilage and tissues. Patients often report a significant reduction in pain and a faster return to their normal activities. Clinical studies and anecdotal evidence from the sports community suggest that PRP can not only accelerate recovery times but also potentially improve the longevity of joint health, offering athletes a valuable tool for both recovery and injury prevention.
By harnessing the body’s own healing capabilities, PRP therapy represents a significant advance in regenerative medicine, providing a safe and effective alternative to more invasive treatments such as surgery.
Exploring Stem Cell Therapy
Definition of Stem Cell Therapy and How It Differs from PRP
Stem Cell Therapy is a groundbreaking approach in regenerative medicine that leverages the body’s own repair mechanisms to treat various degenerative conditions, injuries, and diseases. Unlike PRP, which primarily aids healing through growth factors found in blood platelets, Stem Cell Therapy uses stem cells that have the ability to differentiate into any type of cell needed by the body. This allows for the replacement or repair of damaged tissues with new, functional cells. Stem cells not only initiate repair but also have the potential to restore lost function through the regeneration of whole tissues or organs.
The Process of Stem Cell Therapy: From Harvesting to Re-injection
The process of Stem Cell Therapy typically involves several key steps:
- Harvesting: Stem cells can be collected from several sources within a patient’s body, most commonly from bone marrow or adipose tissue. The collection process varies depending on the source; for example, bone marrow is usually extracted using a needle from the hip bone under local anesthesia.
- Laboratory Processing: Once harvested, the stem cells are sent to a lab where they are isolated and concentrated. During this stage, cells may be cultured to increase their numbers, ensuring there are enough stem cells to have a therapeutic effect when reintroduced into the body.
- Re-injection: The concentrated stem cells are then injected back into the patient’s body at the site of injury or disease. This could be a joint, ligament, or even intravenously, depending on the condition being treated.
Conditions Treated with Stem Cell Therapy
Stem Cell Therapy is utilized in the treatment of a wide array of conditions, highlighting its vast regenerative capabilities. These include:
- Orthopedic Conditions: Such as osteoarthritis, rotator cuff tears, and other types of cartilage and bone damage, where stem cells help regenerate cartilage and reduce inflammation.
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: Such as Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis, where stem cells are studied for their potential to regenerate nerve cells and improve neurological function.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Including heart failure, where injected stem cells can regenerate heart muscle cells, improving heart function.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Such as rheumatoid arthritis, where stem cells may modulate the immune system and repair tissues damaged by these conditions.
The diversity of applications showcases stem cells’ unique ability not only to enhance the body’s healing processes but also to regenerate tissues and potentially return function to areas previously thought irreparable. The ongoing research and clinical trials continue to unlock new possibilities, making Stem Cell Therapy a cornerstone of modern regenerative medicine strategies.
Expert Opinions: Navigating Choices in Regenerative Treatments
Insights from Healthcare Professionals
Dr. Todd Peters, a seasoned orthopedic surgeon specializing in regenerative medicine, provides valuable insights into the decision-making process between opting for Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy and Stem Cell Therapy. According to Dr. Peters, the choice largely depends on the nature of the injury or condition, the patient’s overall health, and the desired outcomes.
When to Choose PRP Therapy:
Dr. Peters recommends PRP for patients with mild to moderate injury or tissue damage where inflammation is a primary concern. “PRP is particularly effective for tendonitis, mild arthritis, and sports injuries where accelerated healing is needed,” he notes. The therapy is less invasive and can often be repeated if necessary, making it a versatile option for many patients.
When to Opt for Stem Cell Therapy:
For more severe or chronic conditions, Dr. Peters suggests considering Stem Cell Therapy. “In cases of substantial joint damage, severe osteoarthritis, or injuries where tissue regeneration is required, stem cells offer a more powerful solution,” he explains. Stem cells not only help reduce inflammation but also have the capacity to replace damaged tissue, offering hope for a more definitive recovery.
The Future of Regenerative Treatments
Looking ahead, Dr. Peters is optimistic about the advancements in regenerative medicine, particularly in the field of orthopedics. “The future is incredibly promising,” he states. “We are looking at potentially being able to regenerate whole joints, repair severely damaged nerves, and more effectively treat degenerative diseases without the need for invasive surgeries.”
In addition to orthopedic applications, regenerative treatments are poised to transform other medical fields. Innovations in bioengineering, such as 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs, and improvements in stem cell cultivation techniques, are expanding the possibilities. These advancements could one day lead to widespread applications in treating cardiovascular, neurological, and autoimmune diseases.
Dr. Peters also highlights the importance of an integrated approach: “As we better understand the molecular and cellular mechanisms behind regeneration, combining stem cell therapy with other modalities, such as gene therapy and personalized medicine, will likely yield even more impressive results.”
Conclusion
The insights from healthcare professionals like Dr. Peters not only guide patients in choosing the right regenerative treatment but also illuminate the path forward for research and application in this dynamic field. With each advancement, the potential of regenerative medicine continues to grow, offering new hope for treatments that were once considered beyond reach.
Safety, Side Effects, and Regulatory Considerations
Safety Profiles of PRP vs Stem Cell Therapy
Both PRP and Stem Cell Therapies are considered safe, particularly because they use the patient’s own biological materials, which minimizes the risk of allergic reactions or immune rejection. However, as with any medical procedure, there are potential risks and side effects.
- PRP Therapy: Commonly reported side effects are minor and include pain at the injection site, swelling, and bruising. These symptoms typically resolve within a few days. The risk of infection is low since the procedure is performed under sterile conditions.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Similar to PRP, the side effects include swelling, bruising, and pain at the injection site. There is also a theoretical risk of forming ectopic tissue, where stem cells differentiate into unintended cell types. However, this is extremely rare with autologous treatments. Advanced techniques in cell processing and reinjection are designed to mitigate these risks.
Regulatory Considerations
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a critical role in regulating medical treatments, including PRP and Stem Cell Therapies. The FDA classifies PRP as a minimally manipulated autologous product under Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act, which means it does not require FDA approval when used in a manner consistent with their homologous use.
Stem Cell Therapies, particularly those involving more than minimal manipulation of the cells, fall under more stringent regulations. Treatments must adhere to FDA guidelines to ensure they are safe and effective. The FDA requires that new stem cell therapies undergo rigorous clinical trials before receiving approval for general use.
Choosing the Right Therapy
When considering whether PRP or Stem Cell Therapy is right for you, consider the following guidelines:
- Assess the Condition: PRP is generally suitable for acute injuries and mild to moderate degenerative conditions, while Stem Cell Therapy may be more appropriate for severe degenerative conditions and cases where structural tissue repair is needed.
- Consult Healthcare Providers: Always discuss potential treatments with healthcare providers who specialize in regenerative medicine. They can provide detailed assessments based on your medical history, current health, and treatment expectations.
- Understand the Treatment: Be aware of what each therapy involves, including the procedures, potential outcomes, and recovery time. Understanding the science behind each option and the realistic outcomes can help in making an informed decision.
Breathe’s Role
Breathe connects patients with qualified experts in regenerative medicine. Through Breathe, you can:
- Access a curated network of specialists who are vetted and have a track record of successful treatments.
- Receive comprehensive information about PRP and Stem Cell Therapies, including detailed FAQs, expert interviews, and patient testimonials.
- Schedule consultations with leading practitioners to discuss your specific needs and get personalized advice.
Both PRP and Stem Cell Therapies offer exciting possibilities for treating a variety of conditions, choosing the right therapy involves understanding the nuances of each treatment, considering your specific health situation, and consulting with experienced medical professionals.
Conclusion
The advancements in regenerative medicine, particularly through PRP (Platelet Rich Plasma) and Stem Cell Therapy, present significant opportunities to enhance quality of life. These therapies harness the body’s own healing mechanisms to repair and regenerate tissues that have been damaged by injury, degeneration, or disease. PRP Therapy, with its focus on using concentrated growth factors, is well-suited for treating acute injuries and mild degenerative conditions. On the other hand, Stem Cell Therapy offers profound regenerative capabilities that can tackle more severe conditions by promoting the growth of new, healthy tissue.
Both treatments offer a promising alternative to more invasive procedures, potentially reducing the need for surgical interventions and the associated recovery times. The key to these therapies is not just their ability to treat symptoms but to address underlying issues, potentially leading to long-lasting relief and improved functionality.
For those interested in exploring the potential of PRP or Stem Cell Therapy, Breathe offers resources to connect you with local experts in regenerative medicine. Our platform facilitates access to top specialists who can offer detailed insights and evaluations tailored to your health needs.
- Visit [Breathe’s Specialist Network]: Explore our comprehensive directory of vetted healthcare providers specializing in PRP and Stem Cell Therapy.
- Schedule a Consultation: Take the first step towards understanding how these therapies can benefit you by booking an appointment with a regenerative medicine expert.
Whether you are dealing with a chronic condition, recovering from an injury, or seeking to improve your overall health and vitality, PRP and Stem Cell Therapies might offer the healing potential you need. We encourage you to reach out through Breathe to learn more and to make informed decisions about your health and wellness journey.
Reed Berglund is a passionate advocate for wellness and an embodiment of the active lifestyle. As a former college athlete who played basketball for the UNLV Running Rebels, he's lived a life deeply immersed in body movement and sports. Reed's enthusiasm for staying active extends far beyond the basketball court. He's an avid surfer, wakeboarder, skier, basketball and tennis enthusiast, and an emerging padel player. His love for holistic well-being also includes a dedication to cold plunges and contrast therapy, embracing these practices to optimize recovery and vitality. In his role as the founder of Breathe, Reed brings his extensive experience in wellness and his unwavering commitment to helping individuals discover their path to a healthier, more mindful life. His personal journey and multifaceted fitness background inspire his vision for Breathe as a platform that empowers urban dwellers to explore, experience, and embrace well-being in all its forms. Reed's current focus lies in the realm of flexibility, a key component in his fitness journey to extend the longevity of his active lifestyle. Through Breathe, he aims to share his passion, knowledge, and insights with a vibrant community of wellness enthusiasts, experts, and storytellers, collectively working toward a healthier and happier world.







